 A new type of architecture has been infiltrating the traditional world for years; homes, condominiums, offices, and all other manner of buildings are being built from industrial storage containers that we would normally see on the back of an 18-wheeler or a shipping barge. The containers are easily stacked, and work quite well for the inhabitants once they are properly insulated, and turned into homes.
A new type of architecture has been infiltrating the traditional world for years; homes, condominiums, offices, and all other manner of buildings are being built from industrial storage containers that we would normally see on the back of an 18-wheeler or a shipping barge. The containers are easily stacked, and work quite well for the inhabitants once they are properly insulated, and turned into homes.
These new structures are subtly environmentally-friendly, in the most obvious way. We are all familiar with the chant “Reduce, re-use, recycle,” and this type of construction is a legitimate way of re-using the excess industrial storage containers that are finished with their initial use.
Shipping container architecture has been around for several years, but this topic presently comes to light again because the American firm Lot-EK, once again, takes it to a new level. 
Their soon-to-be constructed Anyang Public Art Project (APAP) Open Art school in Korea has made news, and that’s not surprising at all upon taking a look. This is a project meant to engage the local community with its open structure, including an amphitheater layout, leading down to the river it is set along. The building will feature offices, open galleries, open meeting space, as well as work space for researchers; as has been the trend with these buildings, the non-traditional shape takes nothing away from the functionality of the new structure. These structures are a method of waste-management that results in beautification and functionality wherever they are planted: The ultimate re-use!



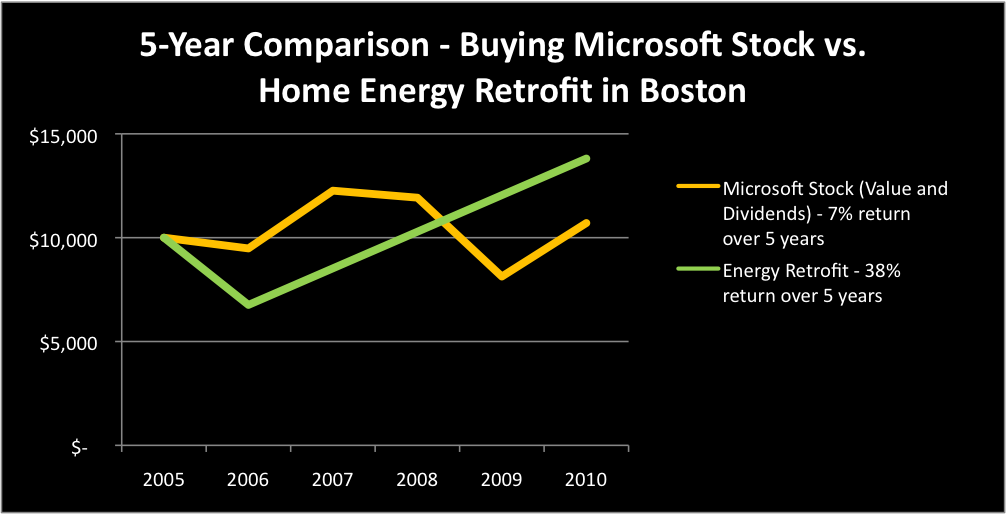



 China exceeded U.S. investment in clean energy for the first time last year with deployments totaling $34.6 billion. The country still has a long way to go to clean up it’s emissions—China surpassed the US as the global leader in C02 emissions several years ago—but they’re moving quickly to clean up their act.
China exceeded U.S. investment in clean energy for the first time last year with deployments totaling $34.6 billion. The country still has a long way to go to clean up it’s emissions—China surpassed the US as the global leader in C02 emissions several years ago—but they’re moving quickly to clean up their act.