Cambridge! It’s finally here: a chance to vividly see the cool or warm air leaving your drafty home, without having to pay hefty fees to a thermal photographer. Thanks to the Thermal Imaging Project on which HEET has partnered with Sagewell Inc., Cambridge homeowners can request thermal (infrared) images of the outsides of their homes.
The images are taken with car-mounted cameras similar to those used for Google Maps street view, and taken on a “first come, first served” basis – with highest priority given to locations with highest demand. With the slight air of a Groupon deal, Sagewell has asked for 400 requests from Cambridge before they will release our thermal images for free.
Because of fossil fuel prices skyrocketing and scientists projecting Cambridge’s summer temperatures will soon start looking more like Atlanta, GA temps, everyone’s heating AND cooling bills are only on their way up. High efficiency in your home is valid for every season.
Even better, the easiest time to work on your home’s energy efficiency is spring and summer, when the wait for weatherization services is short!
Request yours on Sagewell.com now.
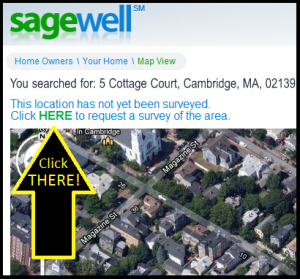
It should take about a minute to do so; just enter your address at the bottom of the home page, hit enter, and then enter your information on the next page that shows up by clicking the green “HERE” (see following photo).
There have already been over 100 requests for thermal images, so if 300 are generated in the next month, everyone will get to have this great service free of cost. Tell your neighbors! We all want to save money and live a little lighter on the planet, don’t we?
The Extra Goods
You and other homeowners, condo owners, and landlords can access their images and an individualized report free of charge online via a password-protected account when the images are available (Sagewell will email you a link). The individualized report shows what to work on, how much it will save you, and connects you with the needed free and rebated services. Commercial building owners and owners of more than one building will be able to view their images and analysis for a small fee.
Not all buildings can be analyzed (due to blocked views from trees, etc. or private way constraints), but Sagewell has agreed to image around 22,000 buildings in Cambridge!
The Thermal Imaging Project will enable residential and commercial building owners to lower costs while supporting our city’s climate and emission reduction goals. One more great tool to wield for average citizens and environmental warriors alike. Get to http://www.Sagewell.com now!
If you have any remaining questions, please contact Sagewell at info@Sagewell.com or HEET at heet.cambridge@gmail.com.